ESG and Impact Investing in 2023/24
Impact investing, also referred to as social, environmental, or social and governance (ESG) investing, is a powerful strategy that blends financial ambitions with a passion for creating a positive societal impact. It's a style of investing that traces its roots back to the Religious Society of Friends, or the Quakers. In 1758, the Quaker Philadelphia Yearly Meeting set a historic precedent by prohibiting members from the inhumane trade of buying or selling humans - arguably marking the inception of socially conscious investing.
From those early beginnings, religious institutions have led the charge in impact and social investing. Today, in 2023, Socially Responsible Investing (SRI), ESG investing, and Impact Investing have moved from the periphery to the heart of mainstream investment strategies. Investors are increasingly mindful of the importance of environmental, social, and governance factors in their investment decisions, and they eagerly seek opportunities that yield positive social and environmental impact alongside financial gains.
Efforts are ongoing to establish standardized ESG frameworks and reporting, while robust impact measurement methodologies are in development to effectively track the outcomes of impact investments. Creative Investment has been at the forefront of these advancements, pioneering the development of standard reporting frameworks and impact measurement with the introduction of the Fully Adjusted Return Methodology in 1990 (detailed in Impact Investing and Capability Statement below). ESG and Impact Investing have thus evolved into indispensable components of the investment landscape, empowering investors to align their portfolios with their values and proactively contribute to addressing global challenges.
Our Solutions and Competencies
We pride ourselves on our strong business competencies, detailed in our Capability Statement, below. Our key service areas include Impact Services: Impact Investing. For further insights, visit our page on Black People and ESG/Impact Investing.
Our Business Competencies: Capability Statement
Impact Services: Impact Investing.
Also See: Black People and ESG/Impact Investing.
ESG/SRI/Impact Investing Strategies
In general, ESG, SRI and impact investors favor:

ESG & Impact Investing Tactics
Social and impact investors use four basic tactics to maximize financial return and attempt to maximize social return. These are outlined below.
SCREENING excludes certain securities from investment consideration based on social and/or environmental criteria. For example, many socially responsible investors screen out tobacco company investments. This is an example of a social screen at work.
DIVESTING is the act of removing stocks from a portfolio based on mainly ethical, non- financial reasons. An investor divests upon realizing that, at some point, ?the cup of endurance runs over, and (is)..no longer willing to be plunged into an abyss of despair? over certain business activities of a corporation. Recently, CalSTRS (California State Teachers' Retirement System) announced the removal of more than $237 million in tobacco holdings from its investment, portfolio after 6 months of financial analysis and deliberations.
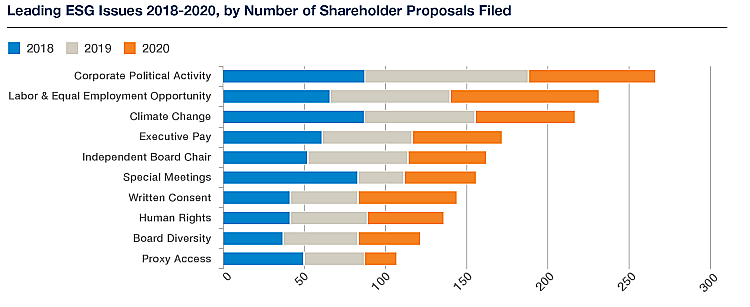
SHAREHOLDER ACTIVISM. Shareholder Activism efforts attempt to positively influence corporate behavior. These efforts include initiating conversations with corporate management, or dialoging, on issues of concern, and submitting and voting proxy resolutions. These activities are undertaken with the belief that social investors, working cooperatively, can steer management on a course that will improve financial performance over time and enhance the well being of the stockholders, customers, employees, vendors, and communities.
POSITIVE IMPACT INVESTING involves making investments in activities and companies believed to have a high and positive social impact. Positive investing activities tend to target underserved communities. These efforts support activities designed to provide mortgage and small business credit to minority and low-income communities. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, passed in 2017, created new tax incentives for investments in what are known as Opportunity Zones: targeted areas in the United States. Investments are made via Qualified Opportunity Funds, who are directed to promote economic development in 8,700 disadvantaged rural and urban (read Native, African American and Hispanic) communities (low-income census tracts selected by state governors and certified by the U.S. Treasury Department) by offering investors substantial federal tax advantages.
The Soaring Trajectory of Impact and ESG Investing
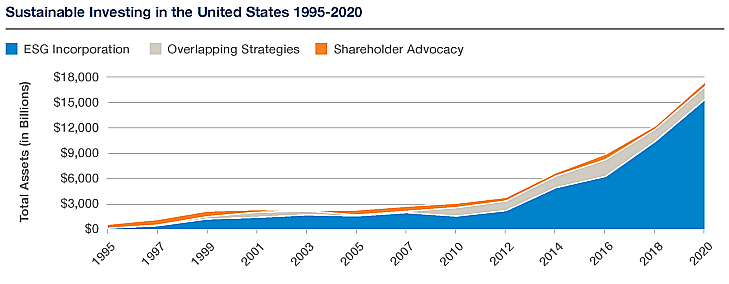
Between 2002 and 2020, the sector of Impact and ESG investing demonstrated strong and consistent growth. However, by 2020, this growth was not just solid — it was skyrocketing. The US SIF Foundation reports that the market began 2020 with "$16.6 trillion in US-domiciled assets." These assets were managed by a substantial number of institutions: 530 institutional investors, 384 money managers, and 1,204 community investment institutions. All these institutions practiced 'ESG incorporation', applying various environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria in their investment analysis and portfolio selection.
Further testament to the growing momentum of ESG investing, the US SIF Trends Report 2020 noted an additional "$2.0 trillion in US-domiciled assets at the start of 2020," held by 205 institutional investors or money managers.
To provide some perspective, when the US SIF Foundation first quantified the US sustainable investment universe in 1995, the total assets stood at a mere $639 billion. Since then, the assets have multiplied over 25 times, signifying a compound annual growth rate of 14 percent. The most impressive acceleration, however, has been observed since 2012.
From 1995 to 2018, the universe of Impact/SRI investing ballooned nearly 18-fold, marking a compound annual growth rate of 13.6 percent. Of this total, a hefty $2.6 trillion in assets were managed via registered investment companies like mutual funds, exchange traded funds, variable annuities, and closed-end funds. This exponential growth signals a promising future for Impact and ESG investing, highlighting its ever-increasing importance in our financial landscape.
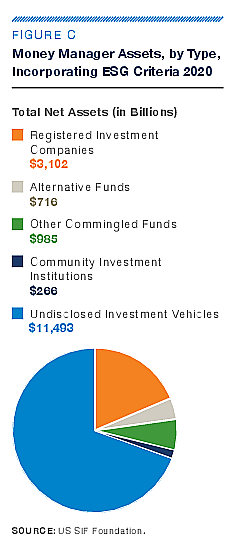
Number of money managers incorporating ESG and Impact Strategies
In 2020, "the US SIF Foundation identified 384 money managers and 1,204 community investing institutions incorporating ESG criteria into their investment analysis and decision-making processes. The $16.6 trillion in ESG incorporation assets they represent is a nearly 43 percent increase over the $11.6 trillion in such assets identified in 2018.
The significant growth in Impact/social/ESG assets reflects several factors. These include growing market penetration of Impact and SRI products, the development of new products that incorporate ESG criteria and the incorporation of ESG criteria by numerous large asset managers across wider portions of their holdings. Furthermore, the past four years have seen new disclosure requirements on the part of numerous institutional investors and asset managers on how they are implementing the UN Sustainable Development Goals, a collection of 17 global goals set by the United Nations General Assembly in 2015 for the year 2030. The Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI), a global framework for taking ESG considerations into account in investment analysis, decision making and active ownership strategies, is another impactful set of guidelines; See our letter to the UN PRI on the US Security and Exchange Commission research on shareholder wealth effects urging pension funds to reject a flawed analysis of shareholder proposals.

